Overview
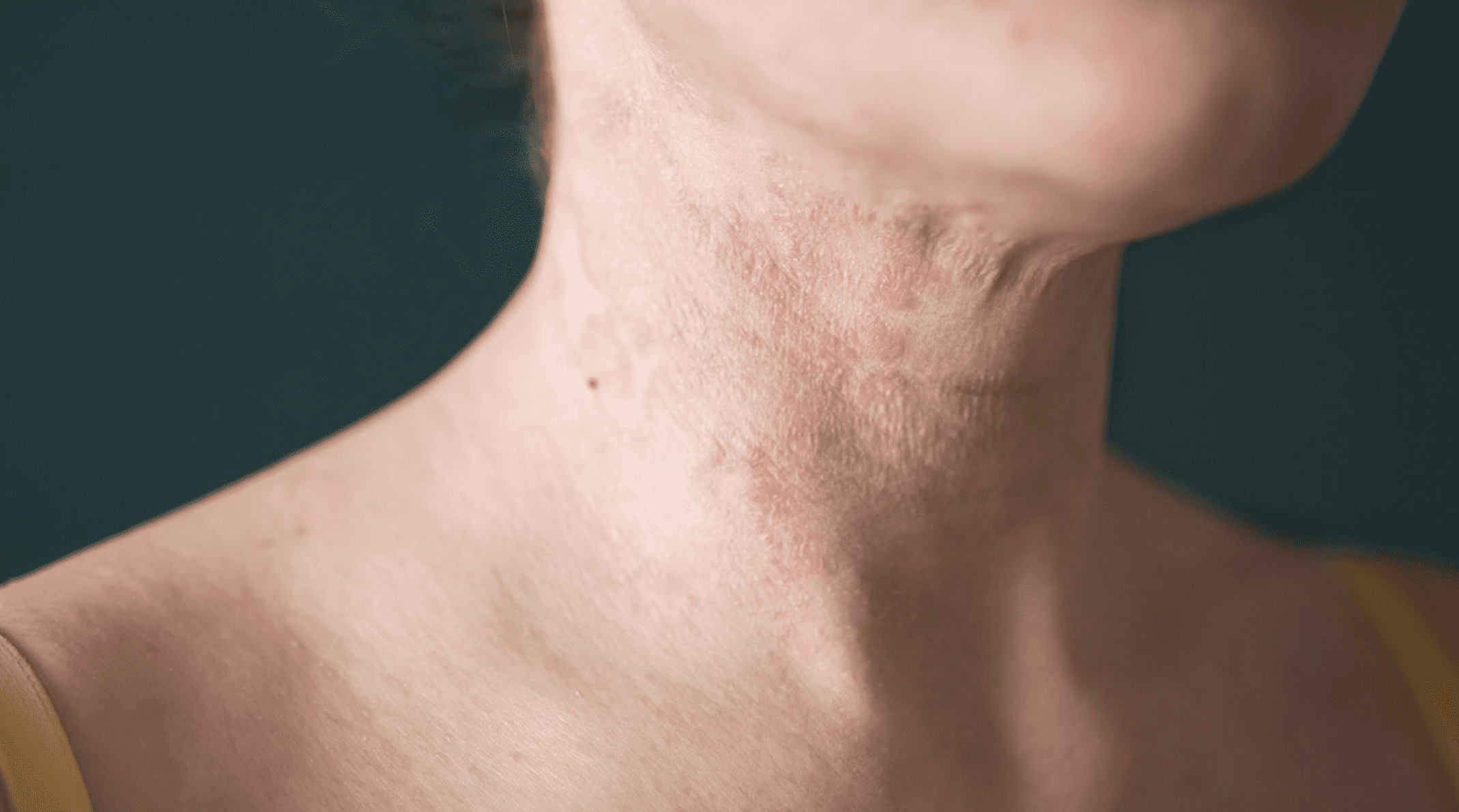
Do you often feel your skin getting dry and inflamed especially during the winter season? It might be an indication of Eczema, an inflammatory skin condition also called Atopic Dermatitis. Eczema is a debilitating skin disease that leaves an ever-lasting impact on one’s physical and mental health. It manifests as red, scaly, itchy skin. There is no definite cure for Eczema, however, many Clinical Research Organizations are trying to find a potential treatment option for Eczema.
In this blog, we will be focusing on Eczema, its causes, treatments, and how it affects the mental and physical health of an individual.
What Are The Causes Of Eczema?
Eczema damages the skin barrier, which aids in shielding us from numerous viruses and dust particles that could infiltrate our skin and lead to illnesses. As a result, our skin is more vulnerable and susceptible to the outside environment.
Atopic Dermatitis, also known as Eczema, is neither harmful nor communicable. The illness can be effectively treated with the right management. Among the contributing elements to eczema are:
- Immune system:
Eczema causes your immune system to become sensitive, even reacting to little allergens or irritants.
- Genetics:
You are more likely to acquire eczema or atopic dermatitis if your family has a history of the condition. Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema may also be more likely to develop if you have a family history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. Dander, animal hair, likewise, allergic reactions to food might occur. Furthermore, there might be a genetic variance that controls a protein that supports the maintenance of healthy skin in your body. If specific proteins are not present in regular amounts, your skin won’t receive the full nourishment it needs.
- Environment:
A number of environmental factors can disrupt your skin’s protective barrier, resulting in eczema or atopic dermatitis. Air pollution, smoking, and exposure to harsh chemicals are a few of these.
- Stress:
Both physical and emotional stress can cause flare-ups of your eczema.
Symptoms of Eczema
The main sign of eczema is irritated, dry, flaky, inflamed, and itchy skin. It can erupt, subside, and then erupt again. The scalp, cheeks, inner elbows, backs of the knees, and arms are the most common areas where eczema manifests itself, yet it can affect any part of the body. It is not communicable and can sometimes get softer as you get older.
Additionally, there may be:
- Noticeable itching.
- Reddish or reddish-gray patches.
- Infection, is indicated by tiny, elevated lumps that, when scratched, exude fluid when they are encrusted.
- Skin that is thick, scaly, and hurts or feels raw.
Many patients are aware that their symptoms worsen at night, making it difficult for them to get any rest. Eczema scratching can exacerbate skin inflammation and discomfort. This could lead to infections that need antibiotic therapy. Sometimes avoiding irritants and moisturizing skin at home is enough to treat mild eczema.
Impact of Eczema On Mental and Physical Health
Eczema and atopic dermatitis are common conditions. Up to 15 million Americans may have this skin condition. It can be too demanding to put up with.
Your eczema might occasionally go away. Remission is the term used to describe this stage. This is referred to as a “flare-up” at other times when it gets worse. Treatment seeks to prevent these episodes from occurring, preventing the deterioration of your symptoms. You can considerably reduce your symptoms by avoiding triggers, moisturizing your skin, taking your medicine, and adhering to any additional directions from a healthcare expert.
Eczema or atopic dermatitis has a significant impact on a person’s mental health in addition to their physical health. Skin-related stigma causes loss of trust and social isolation, lack of confidence, and social isolation. The most noticeable organ of the body, the skin, can provide crucial information about one’s health. Because of this, many who are impacted find it challenging to interact with others and instead choose to withdraw.
Impact Of Eczema
Although it usually affects children, eczema can persist into maturity as was previously mentioned. There are other risk factors connected to eczema, such as:
- Females,
- If you have hay fever or asthma, and
- If you have a history of hay fever, as well as dermatitis or other sensitive skin conditions.
Do Autoimmune Diseases Include Eczema?
Although eczema alone is not an autoimmune disorder, it is frequently linked to other autoimmune conditions such as celiac disease, vitiligo, chronic urticaria, alopecia areata, etc. The immune system may be sensitive to some allergens, but Eczema does not predominantly fall under the umbrella of autoimmune diseases.
What Does Research Suggest For Eczema Treatment?
One of the greatest treatment strategies, according to research, involves wet therapy together with incorporating proper body care and regular hygiene habits. Three daily showers are part of the wet therapy. A topical cream or moisturizer is used to maintain the skin, keep the body hydrated and stop it from drying out and cracking.
How Can We Manage Eczema At Home?
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing may help reduce eczema-related itching.
- Shorten your fingernails.
- Avoid getting too hot since this might cause flare-ups.
- Children should consume extra water to hydrate their skin.
- To prevent flare-ups, identify the triggers and get rid of them from your home.
- Lukewarm water baths.
- Eczema is strongly triggered by stress, adopt stress-reduction strategies. This could entail doing various exercises, taking deep breaths, or consulting a therapist.
Treatment Options For Eczema
The optimal course of treatment for you will depend on the type and severity of your eczema. Combining several therapies might be effective. Generally speaking, there are two types of treatment that can be beneficial: medication and light or UV therapy.
Medication:
Orally available over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines aid to lessen itching. They work by halting allergic reactions brought on by histamine. They can make you drowsy, so it’s better to take them when you don’t need to be awake.
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, your doctor may advise either low or high-dosage steroids.
Another family of medications used to stop the immune system from responding is known as immunosuppressants. This might prevent flare-ups of eczema or atopic dermatitis.
Light Therapy:
Light therapy can assist in preventing the immune system reaction that leads to eczema or atopic dermatitis. It aids in the fight against bacterial infections as well.
The Takeaway:
Eczema, as it goes without saying, is a crippling ailment that negatively affects a person’s mentality. Since mental health is equally important to one’s physical health, it is crucial to take care of it. Eczema can negatively affect one’s mental health because it can cause self-image issues. This can also have a significant negative effect on one’s physical health.
Even though medical science is developing, there is still a long way to go before a permanent cure for this ailment can be discovered. Nevertheless, research groups in the US are working to identify viable treatment options by conducting Paid Clinical Trials for Eczema in Michigan and evaluating the efficacy of those experimental medications on humans.